アダプター
アダプターは、すべてのクライアントまたはクライアントのサブセットにイベントをブロードキャストする役割を担うサーバーサイドコンポーネントです。
複数の Socket.IO サーバーにスケーリングする場合、イベントがすべてのクライアントに適切にルーティングされるように、デフォルトのインメモリアダプターを別の実装に置き換える必要があります。
私たちのチームによってメンテナンスされているアダプターのリストは次のとおりです。
- Redis アダプター
- Redis Streams アダプター
- MongoDB アダプター
- Postgres アダプター
- Cluster アダプター
- Google Cloud Pub/Sub アダプター
- AWS SQS アダプター
- Azure Service Bus アダプター
(素晴らしい!)コミュニティによってメンテナンスされている他のいくつかのオプションもあります。
複数の Socket.IO サーバーと HTTP ロングポーリングを使用する場合、スティッキーセッションを有効にする必要があります。詳細はこちら こちら。
API
アダプターインスタンスには以下でアクセスできます。
// main namespace
const mainAdapter = io.of("/").adapter; // WARNING! io.adapter() will not work
// custom namespace
const adminAdapter = io.of("/admin").adapter;
socket.io@3.1.0 以降、各アダプターインスタンスは次のイベントを発行します。
create-room(引数: room)delete-room(引数: room)join-room(引数: room, id)leave-room(引数: room, id)
例
io.of("/").adapter.on("create-room", (room) => {
console.log(`room ${room} was created`);
});
io.of("/").adapter.on("join-room", (room, id) => {
console.log(`socket ${id} has joined room ${room}`);
});
エミッター
ほとんどのアダプター実装には、関連付けられたエミッターパッケージが付属しており、別の Node.js プロセスから Socket.IO サーバーのグループと通信できます。
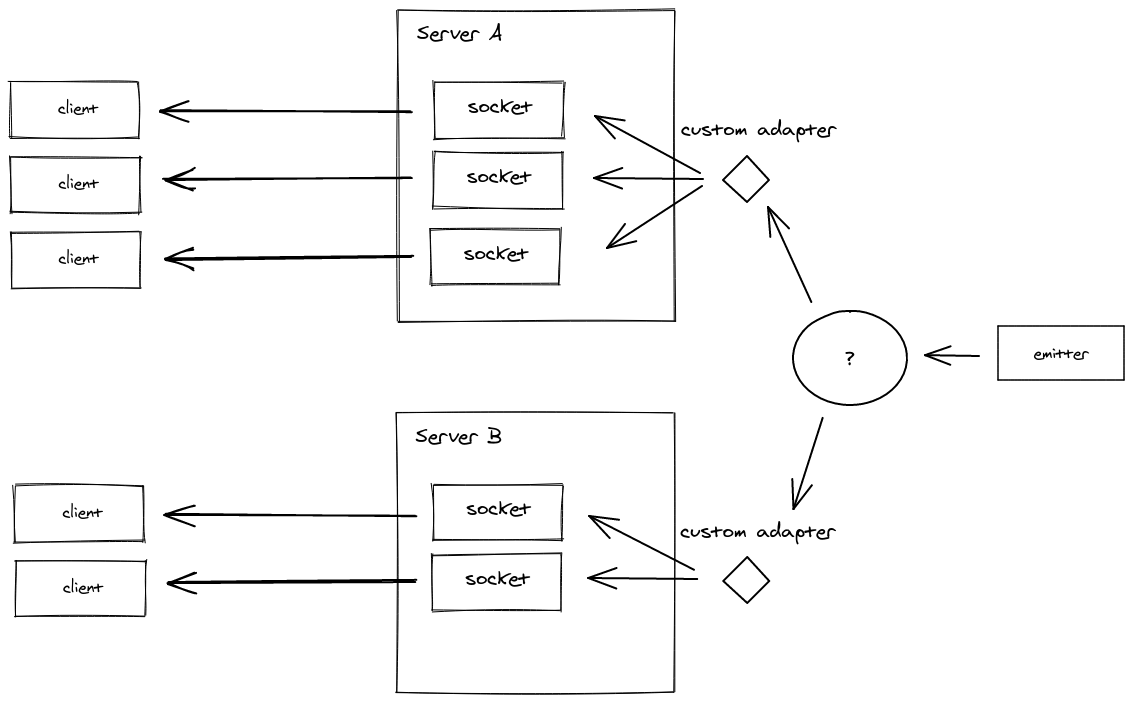
これは、たとえば、すべてのクライアントがマイクロサービス M1 に接続し、マイクロサービス M2 がエミッターを使用してパケットをブロードキャストする(単方向通信)マイクロサービスセットアップで役立つ場合があります。
エミッターチートシート
// to all clients
emitter.emit(/* ... */);
// to all clients in "room1"
emitter.to("room1").emit(/* ... */);
// to all clients in "room1" except those in "room2"
emitter.to("room1").except("room2").emit(/* ... */);
const adminEmitter = emitter.of("/admin");
// to all clients in the "admin" namespace
adminEmitter.emit(/* ... */);
// to all clients in the "admin" namespace and in the "room1" room
adminEmitter.to("room1").emit(/* ... */);
エミッターは、socket.io@4.0.0 で追加されたユーティリティメソッドもサポートしています。
socketsJoin()
// make all Socket instances join the "room1" room
emitter.socketsJoin("room1");
// make all Socket instances of the "admin" namespace in the "room1" room join the "room2" room
emitter.of("/admin").in("room1").socketsJoin("room2");
socketsLeave()
// make all Socket instances leave the "room1" room
emitter.socketsLeave("room1");
// make all Socket instances in the "room1" room leave the "room2" and "room3" rooms
emitter.in("room1").socketsLeave(["room2", "room3"]);
// make all Socket instances in the "room1" room of the "admin" namespace leave the "room2" room
emitter.of("/admin").in("room1").socketsLeave("room2");
disconnectSockets()
// make all Socket instances disconnect
emitter.disconnectSockets();
// make all Socket instances in the "room1" room disconnect (and discard the low-level connection)
emitter.in("room1").disconnectSockets(true);
// make all Socket instances in the "room1" room of the "admin" namespace disconnect
emitter.of("/admin").in("room1").disconnectSockets();
// this also works with a single socket ID
emitter.of("/admin").in(theSocketId).disconnectSockets();
serverSideEmit()
// emit an event to all the Socket.IO servers of the cluster
emitter.serverSideEmit("hello", "world");
// Socket.IO server (server-side)
io.on("hello", (arg) => {
console.log(arg); // prints "world"
});