サーバー API
サーバー
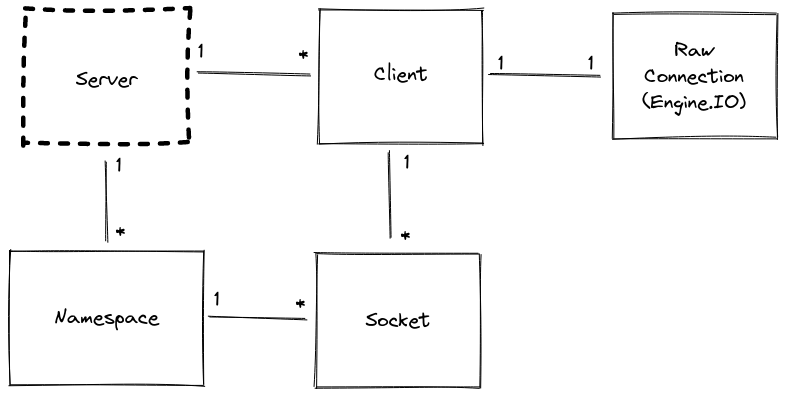
関連ドキュメントページ
コンストラクタ
new Server(httpServer[, options])
httpServer<http.Server>|<https.Server>options<Object>
import { createServer } from "http";
import { Server } from "socket.io";
const httpServer = createServer();
const io = new Server(httpServer, {
// options
});
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
// ...
});
httpServer.listen(3000);
利用可能なオプションの完全なリストはこちらにあります。
new Server(port[, options])
import { Server } from "socket.io";
const io = new Server(3000, {
// options
});
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
// ...
});
利用可能なオプションの完全なリストはこちらにあります。
new Server(options)
options<Object>
import { Server } from "socket.io";
const io = new Server({
// options
});
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
// ...
});
io.listen(3000);
利用可能なオプションの完全なリストはこちらにあります。
イベント
イベント: 'connect'
イベント: "connection"の同義語。
イベント: 'connection'
socket(Socket) クライアントとのソケット接続
クライアントからの接続時に発生します。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
// ...
});
イベント: 'new_namespace'
namespaceNamespace
新しい名前空間が作成されたときに発生します
io.on("new_namespace", (namespace) => {
// ...
});
これは例えば以下の場合に役立ちます
- 各名前空間に共有ミドルウェアをアタッチする場合
io.on("new_namespace", (namespace) => {
namespace.use(myMiddleware);
});
- 動的に作成された名前空間を追跡する場合
io.of(/\/nsp-\w+/);
io.on("new_namespace", (namespace) => {
console.log(namespace.name);
});
属性
server.engine
基盤となる Engine.IO サーバーへの参照。こちらを参照してください。
server.sockets
メインの名前空間(/)のエイリアス。
io.sockets.emit("hi", "everyone");
// is equivalent to
io.of("/").emit("hi", "everyone");
メソッド
server.adapter([value])
アダプターvalueを設定します。デフォルトは、socket.io に付属するメモリベースのAdapterのインスタンスです。socket.io-adapterを参照してください。引数が指定されていない場合、このメソッドは現在の値を返します。
import { Server } from "socket.io";
import { createAdapter } from "@socket.io/redis-adapter";
import { createClient } from "redis";
const io = new Server();
const pubClient = createClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6379 });
const subClient = pubClient.duplicate();
io.adapter(createAdapter(pubClient, subClient));
// redis@3
io.listen(3000);
// redis@4
Promise.all([pubClient.connect(), subClient.connect()]).then(() => {
io.listen(3000);
});
server.attach(httpServer[, options])
httpServer<http.Server>|<https.Server>options<Object>
指定されたoptionsでServerをhttpServerにアタッチします。
import { createServer } from "http";
import { Server } from "socket.io";
const httpServer = createServer();
const io = new Server();
io.attach(httpServer);
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
// ...
});
httpServer.listen(3000);
server.attach(port[, options])
指定されたoptionsでServerを指定されたportにアタッチします。
import { Server } from "socket.io";
const io = new Server();
io.attach(3000);
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
// ...
});
server.attachApp(app[, options])
Socket.IO サーバーをµWebSockets.js アプリにアタッチします
import { App } from "uWebSockets.js";
import { Server } from "socket.io";
const app = App();
const io = new Server();
io.attachApp(app);
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
// ...
});
app.listen(3000, (token) => {
if (!token) {
console.warn("port already in use");
}
});
server.bind(engine)
engine<engine.Server>- **戻り値**
<Server>
上級者向け。サーバーを特定の engine.io Server (または互換性のある API) インスタンスにバインドします。
import { Server } from "socket.io";
import { Server as Engine } from "engine.io";
const engine = new Engine();
const io = new Server();
io.bind(engine);
engine.listen(3000);
server.close([callback])
callback<Function>
Socket.IO サーバーを閉じ、すべてのクライアントを切断します。 callback引数はオプションで、すべての接続が閉じられたときに呼び出されます。
これは、基盤となる HTTP サーバーも閉じます。
import { createServer } from "http";
import { Server } from "socket.io";
const PORT = 3030;
const io = new Server(PORT);
io.close();
const httpServer = createServer();
httpServer.listen(PORT); // PORT is free to use
io.attach(httpServer);
基盤となる HTTP サーバーを閉じるだけでは十分ではありません。新しい接続を受け入れるのを防ぐだけですが、WebSocket で接続されているクライアントはすぐに切断されません。
参照: https://node.dokyumento.jp/api/http.html#serverclosecallback
server.disconnectSockets([close])
v4.0.0 で追加されました
io.of("/").disconnectSockets(close)のエイリアス。
// make all Socket instances disconnect
io.disconnectSockets();
// make all Socket instances in the "room1" room disconnect (and close the low-level connection)
io.in("room1").disconnectSockets(true);
このメソッドは、Postgres アダプターなどの互換性のあるアダプターを使用すると、複数の Socket.IO サーバーのクラスター内でも機能します。
その場合、指定されたノード上のソケットインスタンスにのみ影響を与える場合は、local フラグを使用する必要があります
// make all Socket instances that are currently connected on the given node disconnect
io.local.disconnectSockets();
こちらを参照してください。
server.emit(eventName[, ...args])
履歴
| バージョン | 変更 |
|---|---|
| v4.5.0 | io.emit()がackに対応しました。 |
| v1.0.0 | 初期実装。 |
メインの名前空間内のすべての接続済みクライアントにイベントを送信します。
io.emit("hello");
任意の数の引数を含めることができ、すべてのシリアライズ可能なデータ構造がサポートされています
io.emit("hello", 1, "2", { "3": 4 }, Buffer.from([5]));
受信側では
socket.on("hello", (arg1, arg2, arg3, arg4) => {
console.log(arg1); // 1
console.log(arg2); // "2"
console.log(arg3); // { "3": 4 }
console.log(arg4); // ArrayBuffer or Buffer, depending on the platform
});
引数は自動的にシリアライズされるため、JSON.stringify()を呼び出す必要はありません。
特定のクライアントにパケットを送信するには、to()とexcept()を使用できます
// the “hello” event will be broadcast to all connected clients that are either
// in the "room1" room or in the "room2" room, excluding those in the "room3" room
io.to("room1").to("room2").except("room3").emit("hello");
バージョン4.5.0以降、ブロードキャスト時にackを使用できるようになりました
io.timeout(10000).emit("some-event", (err, responses) => {
if (err) {
// some clients did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
} else {
console.log(responses); // one response per client
}
});
その場合は、timeout()を呼び出す必要があります。
server.emitWithAck(eventName[, ...args])
v4.6.0 で追加されました
eventName<string>|<symbol>argsany[]- **戻り値**
Promise<any[]>
すべての対象クライアントからのackを期待するブロードキャストのPromiseベースのバージョン
try {
const responses = await io.timeout(10000).emitWithAck("some-event");
console.log(responses); // one response per client
} catch (e) {
// some clients did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
}
上記の例は以下と同等です
io.timeout(10000).emit("some-event", (err, responses) => {
if (err) {
// some clients did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
} else {
console.log(responses); // one response per client
}
});
受信側では
socket.on("some-event", (callback) => {
callback("got it"); // only one argument is expected
});
server.except(rooms)
v4.0.0 で追加されました
rooms<string>|<string[]>- **戻り値**
BroadcastOperator
後続のイベント送信の修飾子を設定し、イベントは指定されたroomsに参加していないクライアントにのみ*ブロードキャスト*されます。
// the "foo" event will be broadcast to all connected clients, except the ones that are in the "room-101" room
io.except("room-101").emit("foo", "bar");
// with an array of rooms
io.except(["room-101", "room-102"]).emit("foo", "bar");
// with multiple chained calls
io.except("room-101").except("room-102").emit("foo", "bar");
server.fetchSockets()
v4.0.0 で追加されました
io.of("/").fetchSocket()のエイリアス。
// return all Socket instances of the main namespace
const sockets = await io.fetchSockets();
// return all Socket instances in the "room1" room of the main namespace
const sockets = await io.in("room1").fetchSockets();
使用例
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
const userId = computeUserId(socket);
socket.join(userId);
socket.on("disconnect", async () => {
const sockets = await io.in(userId).fetchSockets();
if (sockets.length === 0) {
// no more active connections for the given user
}
});
});
このメソッドは、Postgres アダプターなどの互換性のあるアダプターを使用すると、複数の Socket.IO サーバーのクラスター内でも機能します。
その場合、指定されたノード上のソケットインスタンスのみを返す場合は、local フラグを使用する必要があります
// return all Socket instances that are currently connected on the given node
const sockets = await io.local.fetchSockets();
こちらを参照してください。
server.in(room)
v1.0.0 で追加されました
server.to(room)の同義語ですが、場合によってはより明確に感じるかもしれません
// disconnect all clients in the "room-101" room
io.in("room-101").disconnectSockets();
server.listen(httpServer[, options])
server.attach(httpServer[, options])の同義語。
server.listen(port[, options])
server.attach(port[, options])の同義語。
server.of(nsp)
nsp<string>|<RegExp>|<Function>- 戻り値
<Namespace>
パス名識別子 nsp で指定された Namespace を初期化し、取得します。名前空間が既に初期化されている場合は、すぐにそれを返します。
const adminNamespace = io.of("/admin");
正規表現または関数を指定して、名前空間を動的に作成することもできます。
const dynamicNsp = io.of(/^\/dynamic-\d+$/).on("connection", (socket) => {
const newNamespace = socket.nsp; // newNamespace.name === "/dynamic-101"
// broadcast to all clients in the given sub-namespace
newNamespace.emit("hello");
});
// client-side
const socket = io("/dynamic-101");
// broadcast to all clients in each sub-namespace
dynamicNsp.emit("hello");
// use a middleware for each sub-namespace
dynamicNsp.use((socket, next) => { /* ... */ });
関数を使用する場合
io.of((name, query, next) => {
// the checkToken method must return a boolean, indicating whether the client is able to connect or not.
next(null, checkToken(query.token));
}).on("connection", (socket) => { /* ... */ });
server.on(eventName, listener)
EventEmitter クラス から継承されています。
eventName<string>|<symbol>listener<Function>- **戻り値**
<Server>
eventName という名前のイベントのリスナー配列の末尾に listener 関数を追加します。
利用可能なイベント
connectionnew_namespaceserverSideEmitメソッドからのカスタムイベント
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
// ...
});
server.onconnection(socket)
socket<engine.Socket>- **戻り値**
<Server>
上級者向け。受信した engine.io(または互換性のある API)Socket から新しい socket.io クライアントを作成します。
import { Server } from "socket.io";
import { Server as Engine } from "engine.io";
const engine = new Engine();
const io = new Server();
engine.on("connection", (socket) => {
io.onconnection(socket);
});
engine.listen(3000);
server.path([value])
engine.io と静的ファイルが提供されるパス value を設定します。デフォルトは /socket.io/ です。引数が指定されていない場合、このメソッドは現在の値を返します。
import { Server } from "socket.io";
const io = new Server();
io.path("/myownpath/");
path の値は、クライアント側の値と一致する必要があります。
import { io } from "socket.io-client";
const socket = io({
path: "/myownpath/"
});
server.serveClient([value])
value が true の場合、接続されているサーバーはクライアントファイルを提供します。デフォルトは true です。このメソッドは、listen が呼び出された後は効果がありません。引数が指定されていない場合、このメソッドは現在の値を返します。
import { Server } from "socket.io";
const io = new Server();
io.serveClient(false);
io.listen(3000);
server.serverSideEmit(eventName[, ...args][, ack])
v4.1.0 で追加
エイリアス: io.of("/").serverSideEmit(/* ... */);
eventName<string>args<any[]>ack<Function>- **戻り値**
true
クラスタの他の Socket.IO サーバーにメッセージを送信します。
構文
io.serverSideEmit("hello", "world");
受信側では
io.on("hello", (arg1) => {
console.log(arg1); // prints "world"
});
確認応答もサポートされています。
// server A
io.serverSideEmit("ping", (err, responses) => {
console.log(responses[0]); // prints "pong"
});
// server B
io.on("ping", (cb) => {
cb("pong");
});
注意事項
connection、connect、new_namespaceという文字列は予約語であり、アプリケーションでは使用できません。任意の数の引数を送信できますが、バイナリ構造は現在サポートされていません(引数の配列は
JSON.stringifyされます)。
例
io.serverSideEmit("hello", "world", 1, "2", { 3: "4" });
- 他の Socket.IO サーバーが一定時間経過後も応答しない場合、確認応答コールバックがエラーで呼び出されることがあります。
io.serverSideEmit("ping", (err, responses) => {
if (err) {
// at least one Socket.IO server has not responded
// the 'responses' array contains all the responses already received though
} else {
// success! the 'responses' array contains one object per other Socket.IO server in the cluster
}
});
server.serverSideEmitWithAck(eventName[, ...args])
v4.6.0 で追加されました
エイリアス: io.of("/").serverSideEmitWithAck(/* ... */);
eventName<string>args<any[]>ack<Function>- **戻り値**
Promise<any[]>
クラスタの他の Socket.IO サーバーからの確認応答を期待するブロードキャストの Promise ベースバージョン。
try {
const responses = await io.serverSideEmitWithAck("some-event");
console.log(responses); // one response per server (except itself)
} catch (e) {
// some servers did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
}
上記の例は以下と同等です
io.serverSideEmit("some-event", (err, responses) => {
if (err) {
// some servers did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
} else {
console.log(responses); // one response per server (except itself)
}
});
受信側では
io.on("some-event", (callback) => {
callback("got it"); // only one argument is expected
});
server.socketsJoin(rooms)
v4.0.0 で追加されました
io.of("/").socketsJoin(rooms) のエイリアス。
// make all Socket instances join the "room1" room
io.socketsJoin("room1");
// make all Socket instances in the "room1" room join the "room2" and "room3" rooms
io.in("room1").socketsJoin(["room2", "room3"]);
// this also works with a single socket ID
io.in(theSocketId).socketsJoin("room1");
このメソッドは、Postgres アダプターなどの互換性のあるアダプターを使用すると、複数の Socket.IO サーバーのクラスター内でも機能します。
その場合、指定されたノード上のソケットインスタンスにのみ影響を与える場合は、local フラグを使用する必要があります
// make all Socket instances that are currently connected on the given node join the "room1" room
io.local.socketsJoin("room1");
こちらを参照してください。
server.socketsLeave(rooms)
v4.0.0 で追加されました
io.of("/").socketsLeave(rooms) のエイリアス。
// make all Socket instances leave the "room1" room
io.socketsLeave("room1");
// make all Socket instances in the "room1" room leave the "room2" and "room3" rooms
io.in("room1").socketsLeave(["room2", "room3"]);
// this also works with a single socket ID
io.in(theSocketId).socketsLeave("room1");
このメソッドは、Postgres アダプターなどの互換性のあるアダプターを使用すると、複数の Socket.IO サーバーのクラスター内でも機能します。
その場合、指定されたノード上のソケットインスタンスにのみ影響を与える場合は、local フラグを使用する必要があります
// make all Socket instances that are currently connected on the given node leave the "room1" room
io.local.socketsLeave("room1");
こちらを参照してください。
server.timeout(value)
v4.5.0 で追加
value<number>- **戻り値**
BroadcastOperator
後続のイベント発行の修飾子を設定します。すべてのターゲットクライアントから確認応答がないまま指定されたミリ秒数が経過すると、コールバックがエラーで呼び出されます。
io.timeout(10000).emit("some-event", (err, responses) => {
if (err) {
// some clients did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
} else {
console.log(responses); // one response per client
}
});
server.to(room)
履歴
| バージョン | 変更 |
|---|---|
| v4.0.0 | 部屋の配列を渡すことができます。 |
| v1.0.0 | 初期実装。 |
room<string>|<string[]>- 戻り値 チェーニング用の
BroadcastOperator
イベントが指定された room に参加しているクライアントにのみ*ブロードキャスト*されるように、後続のイベント発行の修飾子を設定します。
複数の部屋に送信するには、to を複数回呼び出すことができます。
// the “foo” event will be broadcast to all connected clients in the “room-101” room
io.to("room-101").emit("foo", "bar");
// with an array of rooms (a client will be notified at most once)
io.to(["room-101", "room-102"]).emit("foo", "bar");
// with multiple chained calls
io.to("room-101").to("room-102").emit("foo", "bar");
server.use(fn)
v1.0.0 で追加されました
io.of("/").use(fn) のエイリアス。
fn<Function>
メインの名前空間のミドルウェアを登録します。これは、すべての受信 Socket に対して実行される関数であり、パラメータとしてソケットと、オプションで次の登録済みミドルウェアに実行を遅延させる関数を渡します。
ミドルウェアコールバックに渡されたエラーは、特別な connect_error パケットとしてクライアントに送信されます。
サーバー
io.use((socket, next) => {
const err = new Error("not authorized");
err.data = { content: "Please retry later" }; // additional details
next(err);
});
クライアント
socket.on("connect_error", err => {
console.log(err instanceof Error); // true
console.log(err.message); // not authorized
console.log(err.data); // { content: "Please retry later" }
});
詳細についてはこちらをご覧ください。
Express ミドルウェアをお探しの場合は、このセクションをご確認ください。
Namespace
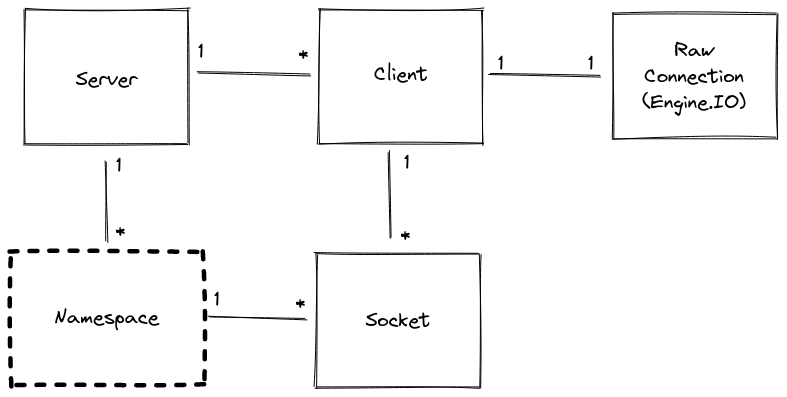
パス名(例:/chat)で識別される特定のスコープ下で接続されたソケットのプールを表します。
詳細についてはこちらをご覧ください。
属性
namespace.adapter
名前空間に使用される "Adapter" です。
注:メインの名前空間のアダプターには、io.of("/").adapter でアクセスできます。
詳細についてはこちらをご覧ください。
const adapter = io.of("/my-namespace").adapter;
namespace.name
名前空間識別子プロパティ。
namespace.sockets
この名前空間に接続されている Socket インスタンスのマップ。
// number of sockets in this namespace (on this node)
const socketCount = io.of("/admin").sockets.size;
イベント
イベント: 'connect'
イベント: "connection" のシノニム。
イベント: 'connection'
socket<Socket>
クライアントからの接続時に発生します。
// main namespace
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
// ...
});
// custom namespace
io.of("/admin").on("connection", (socket) => {
// ...
});
メソッド
namespace.allSockets()
- 戻り値
Promise<Set<SocketId>>
このメソッドは次のメジャーリリースで削除される予定です。serverSideEmit() または fetchSockets() を代わりに使用してください。
この名前空間に接続されているソケット ID のリストを取得します(該当する場合、すべてのノードにわたって)。
// all sockets in the main namespace
const ids = await io.allSockets();
// all sockets in the main namespace and in the "user:1234" room
const ids = await io.in("user:1234").allSockets();
// all sockets in the "chat" namespace
const ids = await io.of("/chat").allSockets();
// all sockets in the "chat" namespace and in the "general" room
const ids = await io.of("/chat").in("general").allSockets();
namespace.disconnectSockets([close])
v4.0.0 で追加されました
close<boolean>基礎となる接続を閉じるかどうか- 戻り値
void
一致する Socket インスタンスを切断します。
// make all Socket instances disconnect
io.disconnectSockets();
// make all Socket instances in the "room1" room disconnect (and discard the low-level connection)
io.in("room1").disconnectSockets(true);
// make all Socket instances in the "room1" room of the "admin" namespace disconnect
io.of("/admin").in("room1").disconnectSockets();
// this also works with a single socket ID
io.of("/admin").in(theSocketId).disconnectSockets();
namespace.emit(eventName[, ...args])
履歴
| バージョン | 変更 |
|---|---|
| v4.5.0 | io.emit()がackに対応しました。 |
| v1.0.0 | 初期実装。 |
指定された名前空間のすべての接続済みクライアントにイベントを送信します。
io.of("/chat").emit("hello");
任意の数の引数を含めることができ、すべてのシリアライズ可能なデータ構造がサポートされています
io.of("/chat").emit("hello", 1, "2", { "3": 4 }, Buffer.from([5]));
受信側では
socket.on("hello", (arg1, arg2, arg3, arg4) => {
console.log(arg1); // 1
console.log(arg2); // "2"
console.log(arg3); // { "3": 4 }
console.log(arg4); // ArrayBuffer or Buffer, depending on the platform
});
引数は自動的にシリアライズされるため、JSON.stringify()を呼び出す必要はありません。
特定のクライアントにパケットを送信するには、to() と except() を使用できます。
// the “hello” event will be broadcast to all connected clients that are either
// in the "room1" room or in the "room2" room, excluding those in the "room3" room
io.of("/chat").to("room1").to("room2").except("room3").emit("hello");
バージョン4.5.0以降、ブロードキャスト時にackを使用できるようになりました
io.of("/chat").timeout(10000).emit("some-event", (err, responses) => {
if (err) {
// some clients did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
} else {
console.log(responses); // one response per client
}
});
その場合、timeout() を呼び出す必要があります.
namespace.emitWithAck(eventName[, ...args])
v4.6.0 で追加されました
eventName<string>|<symbol>argsany[]- **戻り値**
Promise<any[]>
指定された名前空間のすべてのターゲットクライアントからの確認応答を期待するブロードキャストの Promise ベースバージョン
try {
const responses = await io.of("/chat").timeout(10000).emitWithAck("some-event");
console.log(responses); // one response per client
} catch (e) {
// some clients did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
}
上記の例は以下と同等です
io.of("/chat").timeout(10000).emit("some-event", (err, responses) => {
if (err) {
// some clients did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
} else {
console.log(responses); // one response per client
}
});
受信側では
socket.on("some-event", (callback) => {
callback("got it"); // only one argument is expected
});
namespace.except(rooms)
v4.0.0 で追加されました
rooms<string>|<string[]>- **戻り値**
BroadcastOperator
後続のイベント送信の修飾子を設定し、イベントは指定されたroomsに参加していないクライアントにのみ*ブロードキャスト*されます。
const myNamespace = io.of("/my-namespace");
// the "foo" event will be broadcast to all connected clients, except the ones that are in the "room-101" room
myNamespace.except("room-101").emit("foo", "bar");
// with an array of rooms
myNamespace.except(["room-101", "room-102"]).emit("foo", "bar");
// with multiple chained calls
myNamespace.except("room-101").except("room-102").emit("foo", "bar");
namespace.fetchSockets()
v4.0.0 で追加されました
- 戻り値
Socket[]|RemoteSocket[]
一致する Socket インスタンスを返します。
// return all Socket instances in the main namespace
const sockets = await io.fetchSockets();
// return all Socket instances in the "room1" room of the main namespace
const sockets = await io.in("room1").fetchSockets();
// return all Socket instances in the "room1" room of the "admin" namespace
const sockets = await io.of("/admin").in("room1").fetchSockets();
// this also works with a single socket ID
const sockets = await io.in(theSocketId).fetchSockets();
上記の例の sockets 変数は、通常の Socket クラスのサブセットを公開するオブジェクトの配列です。
for (const socket of sockets) {
console.log(socket.id);
console.log(socket.handshake);
console.log(socket.rooms);
console.log(socket.data);
socket.emit(/* ... */);
socket.join(/* ... */);
socket.leave(/* ... */);
socket.disconnect(/* ... */);
}
data 属性は、Socket.IO サーバー間で情報を共有するために使用できる任意のオブジェクトです。
// server A
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
socket.data.username = "alice";
});
// server B
const sockets = await io.fetchSockets();
console.log(sockets[0].data.username); // "alice"
重要な注意:このメソッド(および socketsJoin、socketsLeave、disconnectSockets も)は Redis アダプター(socket.io-redis@6.1.0 以降)と互換性があるため、Socket.IO サーバー間で機能します。
namespace.in(room)
v1.0.0 で追加されました
namespace.to(room)の同義語ですが、場合によってはより明確に感じるかもしれません。
const myNamespace = io.of("/my-namespace");
// disconnect all clients in the "room-101" room
myNamespace.in("room-101").disconnectSockets();
namespace.serverSideEmit(eventName[, ...args][, ack])
v4.1.0 で追加
eventName<string>args<any[]>ack<Function>- **戻り値**
true
クラスタの他の Socket.IO サーバーにメッセージを送信します。
構文
io.of("/chat").serverSideEmit("hello", "world");
受信側では
io.of("/chat").on("hello", (arg1) => {
console.log(arg1); // prints "world"
});
確認応答もサポートされています。
// server A
io.of("/chat").serverSideEmit("ping", (err, responses) => {
console.log(responses[0]); // prints "pong"
});
// server B
io.of("/chat").on("ping", (cb) => {
cb("pong");
});
注意事項
connection、connect、new_namespaceという文字列は予約語であり、アプリケーションでは使用できません。任意の数の引数を送信できますが、バイナリ構造は現在サポートされていません(引数の配列は
JSON.stringifyされます)。
例
io.of("/chat").serverSideEmit("hello", "world", 1, "2", { 3: "4" });
- 他の Socket.IO サーバーが一定時間経過後も応答しない場合、確認応答コールバックがエラーで呼び出されることがあります。
io.of("/chat").serverSideEmit("ping", (err, responses) => {
if (err) {
// at least one Socket.IO server has not responded
// the 'responses' array contains all the responses already received though
} else {
// success! the 'responses' array contains one object per other Socket.IO server in the cluster
}
});
namespace.serverSideEmitWithAck(eventName[, ...args])
v4.6.0 で追加されました
eventName<string>args<any[]>ack<Function>- **戻り値**
Promise<any[]>
クラスタの他の Socket.IO サーバーからの確認応答を期待するブロードキャストの Promise ベースバージョン。
try {
const responses = await io.of("/chat").serverSideEmitWithAck("some-event");
console.log(responses); // one response per server (except itself)
} catch (e) {
// some servers did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
}
上記の例は以下と同等です
io.of("/chat").serverSideEmit("some-event", (err, responses) => {
if (err) {
// some servers did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
} else {
console.log(responses); // one response per server (except itself)
}
});
受信側では
io.of("/chat").on("some-event", (callback) => {
callback("got it"); // only one argument is expected
});
namespace.socketsJoin(rooms)
v4.0.0 で追加されました
rooms<string>|<string[]>- 戻り値
void
一致するSocketインスタンスを指定されたルームに参加させます。
// make all Socket instances join the "room1" room
io.socketsJoin("room1");
// make all Socket instances in the "room1" room join the "room2" and "room3" rooms
io.in("room1").socketsJoin(["room2", "room3"]);
// make all Socket instances in the "room1" room of the "admin" namespace join the "room2" room
io.of("/admin").in("room1").socketsJoin("room2");
// this also works with a single socket ID
io.in(theSocketId).socketsJoin("room1");
詳細はこちらこちらをご覧ください。
namespace.socketsLeave(rooms)
v4.0.0 で追加されました
rooms<string>|<string[]>- 戻り値
void
一致するSocketインスタンスを指定されたルームから退出させます。
// make all Socket instances leave the "room1" room
io.socketsLeave("room1");
// make all Socket instances in the "room1" room leave the "room2" and "room3" rooms
io.in("room1").socketsLeave(["room2", "room3"]);
// make all Socket instances in the "room1" room of the "admin" namespace leave the "room2" room
io.of("/admin").in("room1").socketsLeave("room2");
// this also works with a single socket ID
io.in(theSocketId).socketsLeave("room1");
namespace.timeout(value)
v4.5.0 で追加
value<number>- **戻り値**
BroadcastOperator
後続のイベント送信に対する修飾子をセットします。クライアントからの確認応答がないまま指定されたミリ秒数が経過すると、コールバックがエラーと共に呼び出されます。
io.of("/chat").timeout(10000).emit("some-event", (err, responses) => {
if (err) {
// some clients did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
} else {
console.log(responses); // one response per client
}
});
namespace.to(room)
履歴
| バージョン | 変更 |
|---|---|
| v4.0.0 | 部屋の配列を渡すことができます。 |
| v1.0.0 | 初期実装。 |
room<string>|<string[]>- 戻り値 チェーニング用の
BroadcastOperator
イベントが指定された room に参加しているクライアントにのみ*ブロードキャスト*されるように、後続のイベント発行の修飾子を設定します。
複数の部屋に送信するには、to を複数回呼び出すことができます。
const myNamespace = io.of("/my-namespace");
// the “foo” event will be broadcast to all connected clients in the “room-101” room
myNamespace.to("room-101").emit("foo", "bar");
// with an array of rooms (a client will be notified at most once)
myNamespace.to(["room-101", "room-102"]).emit("foo", "bar");
// with multiple chained calls
myNamespace.to("room-101").to("room-102").emit("foo", "bar");
namespace.use(fn)
v1.0.0 で追加されました
fn<Function>
指定された名前空間のミドルウェアを登録します。これは、受信するすべてのSocketに対して実行される関数であり、パラメータとしてソケットと、オプションで次の登録済みミドルウェアへの実行を遅延させる関数を受け取ります。
ミドルウェアコールバックに渡されたエラーは、特別な connect_error パケットとしてクライアントに送信されます。
サーバー
io.of("/chat").use((socket, next) => {
const err = new Error("not authorized");
err.data = { content: "Please retry later" }; // additional details
next(err);
});
クライアント
socket.on("connect_error", err => {
console.log(err instanceof Error); // true
console.log(err.message); // not authorized
console.log(err.data); // { content: "Please retry later" }
});
詳細についてはこちらをご覧ください。
Express ミドルウェアをお探しの場合は、このセクションをご確認ください。
フラグ
フラグ: 'local'
後続のイベント送信に対する修飾子をセットします。イベントデータは、(複数のノードにスケーリングする場合)現在のノードにのみ*ブロードキャスト*されます。
io.local.emit("an event", { some: "data" });
フラグ: 'volatile'
後続のイベント送信に対する修飾子をセットします。クライアントが(ネットワークの遅延やその他の問題、またはロングポーリングで接続されていてリクエスト-レスポンスサイクルの途中にあるために)メッセージを受信する準備ができていない場合、イベントデータは失われる可能性があります。
io.volatile.emit("an event", { some: "data" }); // the clients may or may not receive it
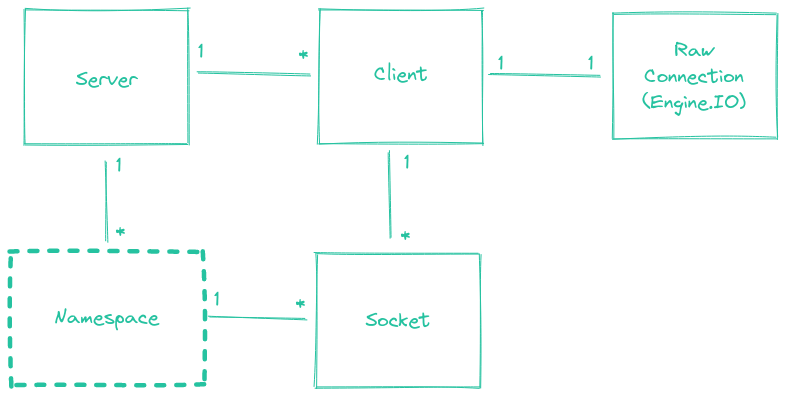
Socket
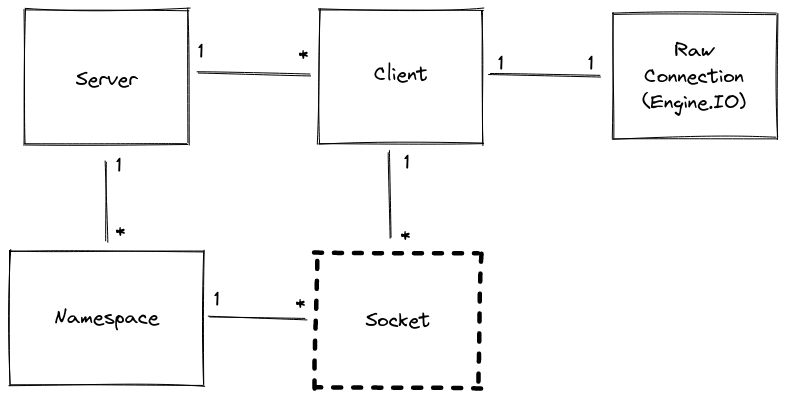
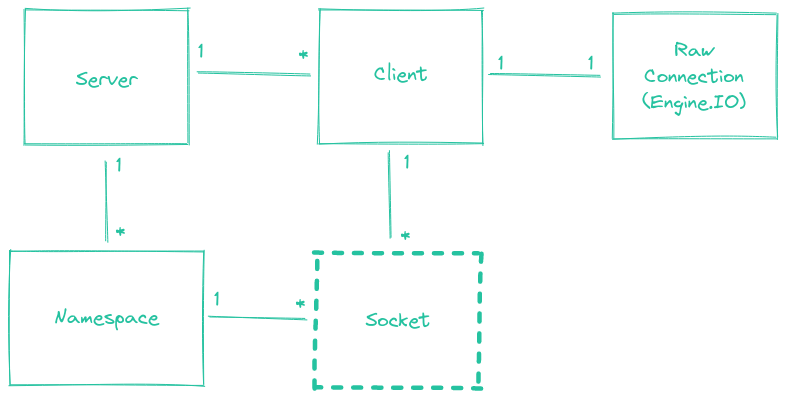
Socketは、ブラウザクライアントと対話するための基本クラスです。Socketは特定のNamespace(デフォルトは/)に属し、基盤となるClientを使用して通信します。
Socketは実際の基盤となるTCP/IP socketとは直接関係がなく、クラスの名前であることに注意してください。
各Namespace内では、Socketが参加および退出できる任意のチャネル(roomと呼ばれます)を定義することもできます。これは、Socketのグループにブロードキャストする便利な方法を提供します(以下のSocket#toを参照)。
SocketクラスはEventEmitterを継承します。Socketクラスはemitメソッドをオーバーライドし、他のEventEmitterメソッドは変更しません。ここに記載されているメソッドのうち、EventEmitterメソッドとしても表示されるもの(emitを除く)はすべてEventEmitterによって実装されており、EventEmitterのドキュメントが適用されます。
詳細はこちらこちらをご覧ください。
イベント
イベント: 'disconnect'
reason<string>切断の理由(クライアント側またはサーバー側)
切断時に発生します。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
socket.on("disconnect", (reason) => {
// ...
});
});
考えられる理由
| 理由 | 説明 |
|---|---|
server namespace disconnect | ソケットはsocket.disconnect()を使用して強制的に切断されました。 |
client namespace disconnect | クライアントがsocket.disconnect()を使用してソケットを手動で切断しました。 |
server shutting down | サーバーがシャットダウン中です。 |
ping timeout | クライアントがpingTimeout遅延内にPONGパケットを送信しませんでした。 |
transport close | 接続が閉じられました(例:ユーザーが接続を失った、またはネットワークがWiFiから4Gに変更された)。 |
transport error | 接続でエラーが発生しました。 |
parse error | サーバーがクライアントから無効なパケットを受信しました。 |
forced close | サーバーがクライアントから無効なパケットを受信しました。 |
forced server close | クライアントが時間内に名前空間に参加せず(connectTimeoutオプションを参照)、強制的に閉じられました。 |
イベント: 'disconnecting'
v1.5.0で追加されました
reason<string>切断の理由(クライアント側またはサーバー側)
クライアントが切断される直前(ただし、まだroomsを退出していない)に発生します。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
socket.on("disconnecting", (reason) => {
console.log(socket.rooms); // Set { ... }
});
});
非同期ハンドラを使用する場合は、rooms属性のコピーを作成する必要があります。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
socket.on("disconnecting", async (reason) => {
const rooms = new Set(socket.rooms);
await someLongRunningOperation();
// socket.rooms will be empty there
console.log(rooms);
});
});
これらのイベントは、connect、connect_error、newListener、removeListenerと共に、アプリケーションでは使用しないでください。
// BAD, will throw an error
socket.emit("disconnect");
属性
socket.client
基盤となるClientオブジェクトへの参照。
socket.conn
<engine.Socket>
基盤となるClientトランスポート接続(engine.io Socketオブジェクト)への参照。これにより、IOトランスポート層にアクセスできます。これは、依然として(大部分)実際のTCP / IPソケットを抽象化しています。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
console.log("initial transport", socket.conn.transport.name); // prints "polling"
socket.conn.once("upgrade", () => {
// called when the transport is upgraded (i.e. from HTTP long-polling to WebSocket)
console.log("upgraded transport", socket.conn.transport.name); // prints "websocket"
});
socket.conn.on("packet", ({ type, data }) => {
// called for each packet received
});
socket.conn.on("packetCreate", ({ type, data }) => {
// called for each packet sent
});
socket.conn.on("drain", () => {
// called when the write buffer is drained
});
socket.conn.on("close", (reason) => {
// called when the underlying connection is closed
});
});
socket.data
v4.0.0 で追加されました
fetchSockets()ユーティリティメソッドと組み合わせて使用できる任意のオブジェクト
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
socket.data.username = "alice";
});
const sockets = await io.fetchSockets();
console.log(sockets[0].data.username); // "alice"
これは、Postgresアダプターのような互換性のあるアダプターを使用することで、Socket.IOクラスター内でも機能します。
socket.handshake
ハンドシェイクの詳細
| フィールド | タイプ | 説明 |
|---|---|---|
| headers | IncomingHttpHeaders | ハンドシェイクの一部として送信されたヘッダー。 |
| time | <string> | 作成日(文字列として)。 |
| address | <string> | クライアントのIPアドレス。 |
| xdomain | <boolean> | 接続がクロスドメインかどうか。 |
| secure | <boolean> | 接続がSSLを介して行われているかどうか。 |
| issued | <number> | 作成日(UNIXタイムスタンプとして)。 |
| url | <string> | リクエストURL文字列。 |
| query | Record<string, string or string[]> | 最初のリクエストのクエリパラメータ。 |
| auth | Record<string, any> | 認証ペイロード。こちらも参照してください。 |
使用方法
io.use((socket, next) => {
let handshake = socket.handshake;
// ...
});
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
let handshake = socket.handshake;
// ...
});
例
const handshake = {
headers: {
"user-agent": "node-XMLHttpRequest",
accept: "*/*",
host: "localhost:3000",
connection: "close"
},
time: "Wed Jan 01 2020 01:00:00 GMT+0100 (Central European Standard Time)",
address: "::ffff:127.0.0.1",
xdomain: false,
secure: false,
issued: 1577836800000,
url: "/socket.io/?EIO=4&transport=polling&t=OPAfXv5&b64=1",
query: {
EIO: "4",
transport: "polling",
t: "OPAfXv5",
b64: "1"
},
auth: {}
}
注:headers属性は、セッションの最初のHTTPリクエストのヘッダーを参照し、後続のHTTPリクエストでは更新されません。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
console.log(socket.handshake.headers === socket.request.headers); // prints "true"
});
socket.id
基盤となるClientから提供される、セッションの一意の識別子。
id属性は、アプリケーションで使用することを意図していない(またはデバッグ目的のみに使用することを意図している)**一時的な** IDです。理由は次のとおりです。
- このIDは、再接続ごとに(たとえば、WebSocket接続が切断された場合、またはユーザーがページを更新した場合)再生成されます。
- 2つの異なるブラウザタブには2つの異なるIDがあります。
- サーバー上に特定のIDのメッセージキューは保存されません(つまり、クライアントが切断された場合、サーバーからこのIDに送信されたメッセージは失われます)。
代わりに、通常のセッションID(Cookieで送信されるか、localStorageに保存されてauthペイロードで送信される)を使用してください。
こちらもご覧ください
socket.recovered
v4.6.0 で追加されました
最後の再接続中に接続状態が正常に回復されたかどうか。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
if (socket.recovered) {
// recovery was successful: socket.id, socket.rooms and socket.data were restored
} else {
// new or unrecoverable session
}
});
この機能の詳細はこちらこちらをご覧ください。
socket.request
基盤となるengine.io Clientを開始したrequestへの参照を返すゲッタープロキシ。CookieやUser-Agentなどのリクエストヘッダーにアクセスするのに役立ちます。
import { parse } from "cookie";
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
const cookies = parse(socket.request.headers.cookie || "");
});
注:socket.requestは、セッションの最初のHTTPリクエストを参照し、後続のHTTPリクエストでは更新されません。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
console.log(socket.request.headers === socket.handshake.headers); // prints "true"
});
この参照が必要ない場合は、メモリフットプリントを削減するために破棄できます。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
delete socket.conn.request;
});
socket.rooms
このクライアントが属するルームを識別する文字列のセット。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
console.log(socket.rooms); // Set { <socket.id> }
socket.join("room1");
console.log(socket.rooms); // Set { <socket.id>, "room1" }
});
メソッド
socket.compress(value)
value<boolean>後続のパケットを圧縮するかどうか- 戻り値 連鎖のための
Socket
後続のイベント送信に対する修飾子をセットします。値がtrueの場合にのみ、イベントデータが*圧縮*されます。メソッドを呼び出さない場合、デフォルトは`true`です。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
socket.compress(false).emit("uncompressed", "that's rough");
});
socket.disconnect([close])
このソケットを切断します。closeの値が`true`の場合、基盤となる接続を閉じます。そうでない場合、名前空間のみを切断します。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
setTimeout(() => socket.disconnect(true), 5000);
});
socket.emit(eventName[, ...args][, ack])
(EventEmitter.emitをオーバーライド)
eventName<string>|<symbol>args<any[]>ack<Function>- **戻り値**
true
文字列名で識別されるソケットにイベントを送信します。他のパラメータを含めることができます。Bufferを含む、すべてのシリアライズ可能なデータ構造がサポートされています。
io.on("connection", () => {
socket.emit("hello", "world");
socket.emit("with-binary", 1, "2", { 3: "4", 5: Buffer.from([6]) });
});
ack引数はオプションであり、クライアントの回答と共に呼び出されます。
サーバー
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
socket.emit("hello", "world", (response) => {
console.log(response); // "got it"
});
});
クライアント
socket.on("hello", (arg, callback) => {
console.log(arg); // "world"
callback("got it");
});
socket.emitWithAck(eventName[, ...args])
v4.6.0 で追加されました
eventName<string>|<symbol>argsany[]- 戻り値
Promise<any>
指定されたクライアントからの確認応答を期待する、Promise ベースの送信バージョンです。
io.on("connection", async (socket) => {
// without timeout
const response = await socket.emitWithAck("hello", "world");
// with a specific timeout
try {
const response = await socket.timeout(10000).emitWithAck("hello", "world");
} catch (err) {
// the client did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
}
});
上記の例は以下と同等です
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
// without timeout
socket.emit("hello", "world", (val) => {
// ...
});
// with a specific timeout
socket.timeout(10000).emit("hello", "world", (err, val) => {
// ...
});
});
受信側では
socket.on("hello", (arg1, callback) => {
callback("got it"); // only one argument is expected
});
socket.eventNames()
EventEmitter から継承されています(ここでは言及されていない他のメソッドも同様です)。events モジュールの Node.js ドキュメントを参照してください。
socket.except(rooms)
v4.0.0 で追加されました
rooms<string>|<string[]>- **戻り値**
BroadcastOperator
後続のイベント送信に対する修飾子を設定します。イベントは、指定された rooms に参加していないクライアント(ソケット自体を除く)にのみブロードキャストされます。
// to all clients except the ones in "room1" and the sender
socket.broadcast.except("room1").emit(/* ... */);
// same as above
socket.except("room1").emit(/* ... */);
// to all clients in "room4" except the ones in "room5" and the sender
socket.to("room4").except("room5").emit(/* ... */);
socket.in(room)
v1.0.0 で追加されました
socket.to(room) の同義語です。
socket.join(room)
room<string>|<string[]>- 戻り値
void|Promise
ソケットを指定された room または部屋のリストに追加します。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
socket.join("room 237");
console.log(socket.rooms); // Set { <socket.id>, "room 237" }
socket.join(["room 237", "room 238"]);
io.to("room 237").emit("a new user has joined the room"); // broadcast to everyone in the room
});
ルームへの参加の仕組みは、設定された Adapter (上記の Server#adapter を参照)によって処理され、デフォルトは socket.io-adapter です。
便宜上、各ソケットは自動的にその ID で識別されるルームに参加します(Socket#id を参照)。これにより、他のソケットにメッセージをブロードキャストすることが容易になります。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
socket.on("say to someone", (id, msg) => {
// send a private message to the socket with the given id
socket.to(id).emit("my message", msg);
});
});
socket.leave(room)
room<string>- 戻り値
void|Promise
ソケットを指定された room から削除します。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
socket.leave("room 237");
io.to("room 237").emit(`user ${socket.id} has left the room`);
});
切断時にルームは自動的に退出されます。
socket.listenersAny()
- 戻り値
<Function[]>
登録されているキャッチオールリスナーのリストを返します。
const listeners = socket.listenersAny();
socket.listenersAnyOutgoing()
v4.5.0 で追加
- 戻り値
<Function[]>
送信パケット用に登録されているキャッチオールリスナーのリストを返します。
const listeners = socket.listenersAnyOutgoing();
socket.offAny([listener])
listener<Function>
以前に登録されたリスナーを削除します。リスナーが指定されていない場合、すべてのキャッチオールリスナーが削除されます。
const myListener = () => { /* ... */ };
socket.onAny(myListener);
// then, later
socket.offAny(myListener);
socket.offAny();
socket.offAnyOutgoing([listener])
v4.5.0 で追加
listener<Function>
以前に登録されたリスナーを削除します。リスナーが指定されていない場合、すべてのキャッチオールリスナーが削除されます。
const myListener = () => { /* ... */ };
socket.onAnyOutgoing(myListener);
// remove a single listener
socket.offAnyOutgoing(myListener);
// remove all listeners
socket.offAnyOutgoing();
socket.on(eventName, callback)
EventEmitter クラス から継承されています。
eventName<string>|<symbol>callback<Function>- 戻り値
<Socket>
指定されたイベントの新しいハンドラーを登録します。
socket.on("news", (data) => {
console.log(data);
});
// with several arguments
socket.on("news", (arg1, arg2, arg3) => {
// ...
});
// or with acknowledgement
socket.on("news", (data, callback) => {
callback(0);
});
socket.onAny(callback)
callback<Function>
新しいキャッチオールリスナーを登録します。
socket.onAny((event, ...args) => {
console.log(`got ${event}`);
});
確認応答はキャッチオールリスナーではキャッチされません。
socket.emit("foo", (value) => {
// ...
});
socket.onAnyOutgoing(() => {
// triggered when the event is sent
});
socket.onAny(() => {
// not triggered when the acknowledgement is received
});
socket.onAnyOutgoing(callback)
v4.5.0 で追加
callback<Function>
送信パケット用に新しいキャッチオールリスナーを登録します。
socket.onAnyOutgoing((event, ...args) => {
console.log(`got ${event}`);
});
確認応答はキャッチオールリスナーではキャッチされません。
socket.on("foo", (value, callback) => {
callback("OK");
});
socket.onAny(() => {
// triggered when the event is received
});
socket.onAnyOutgoing(() => {
// not triggered when the acknowledgement is sent
});
socket.once(eventName, listener)
EventEmitter から継承されています(ここでは言及されていない他のメソッドも同様です)。events モジュールの Node.js ドキュメントを参照してください。
socket.prependAny(callback)
callback<Function>
新しいキャッチオールリスナーを登録します。リスナーはリスナー配列の先頭に追加されます。
socket.prependAny((event, ...args) => {
console.log(`got ${event}`);
});
socket.prependAnyOutgoing(callback)
v4.5.0 で追加
callback<Function>
送信パケット用に新しいキャッチオールリスナーを登録します。リスナーはリスナー配列の先頭に追加されます。
socket.prependAnyOutgoing((event, ...args) => {
console.log(`got ${event}`);
});
socket.removeAllListeners([eventName])
EventEmitter から継承されています(ここでは言及されていない他のメソッドも同様です)。events モジュールの Node.js ドキュメントを参照してください。
socket.removeListener(eventName, listener)
EventEmitter から継承されています(ここでは言及されていない他のメソッドも同様です)。events モジュールの Node.js ドキュメントを参照してください。
socket.send([...args][, ack])
args<any[]>ack<Function>- 戻り値
Socket
message イベントを送信します。socket.emit(eventName[, ...args][, ack]) を参照してください。
socket.timeout(value)
v4.4.0 で追加されました
後続のイベント送信に対する修飾子をセットします。クライアントからの確認応答がないまま指定されたミリ秒数が経過すると、コールバックがエラーと共に呼び出されます。
socket.timeout(5000).emit("my-event", (err) => {
if (err) {
// the client did not acknowledge the event in the given delay
}
});
socket.to(room)
履歴
| バージョン | 変更 |
|---|---|
| v4.0.0 | 部屋の配列を渡すことができます。 |
| v1.0.0 | 初期実装。 |
room<string>|<string[]>- 戻り値 連鎖のための
Socket
後続のイベント送信に対する修飾子を設定します。イベントは、指定された room に参加しているクライアント(ソケット自体を除く)にのみブロードキャストされます。
複数の部屋に送信するには、to を複数回呼び出すことができます。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
// to one room
socket.to("others").emit("an event", { some: "data" });
// to multiple rooms
socket.to("room1").to("room2").emit("hello");
// or with an array
socket.to(["room1", "room2"]).emit("hello");
// a private message to another socket
socket.to(/* another socket id */).emit("hey");
// WARNING: `socket.to(socket.id).emit()` will NOT work
// Please use `io.to(socket.id).emit()` instead.
});
注:ブロードキャスト時には確認応答はサポートされません。
socket.use(fn)
履歴
| バージョン | 変更 |
|---|---|
| v3.0.5 | 最初の実装の復元。 |
| v3.0.0 | socket.onAny() に代わる削除。 |
| v1.7.2 | error イベントはクライアントに直接送信されます。 |
| v1.6.0 | 最初の実装。 |
fn<Function>
ミドルウェアを登録します。これは、すべての受信 Packet に対して実行され、パラメータとしてパケットと、オプションで次の登録済みミドルウェアへの実行を延期する関数を受け取る関数です。
ミドルウェアコールバックに渡されたエラーは、サーバー側で error イベントとして発行されます。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
socket.use(([event, ...args], next) => {
if (isUnauthorized(event)) {
return next(new Error("unauthorized event"));
}
// do not forget to call next
next();
});
socket.on("error", (err) => {
if (err && err.message === "unauthorized event") {
socket.disconnect();
}
});
});
フラグ
フラグ: 'broadcast'
後続のイベント送信に対する修飾子を設定します。イベントデータは送信者以外のすべてのソケットにのみ*ブロードキャスト*されます。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
socket.broadcast.emit("an event", { some: "data" }); // everyone gets it but the sender
});
フラグ: 'volatile'
後続のイベント送信に対する修飾子を設定します。クライアントがネットワークの遅延やその他の問題、またはロングポーリングを介して接続されていてリクエスト-レスポンスサイクルの途中にあるためにメッセージを受信する準備ができていない場合、イベントデータは失われる可能性があります。
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
socket.volatile.emit("an event", { some: "data" }); // the client may or may not receive it
});
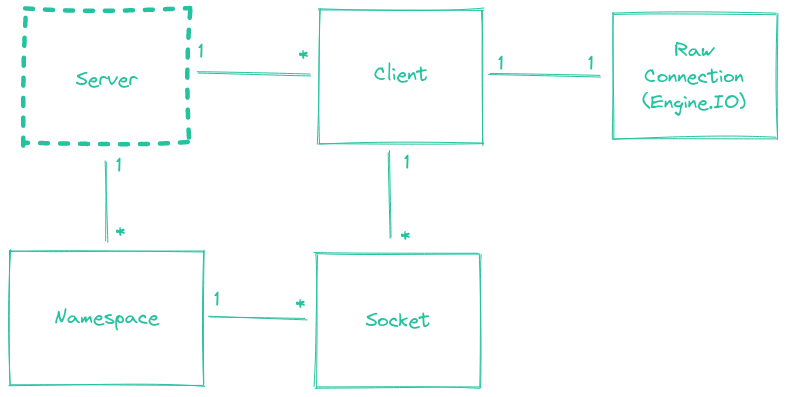
クライアント
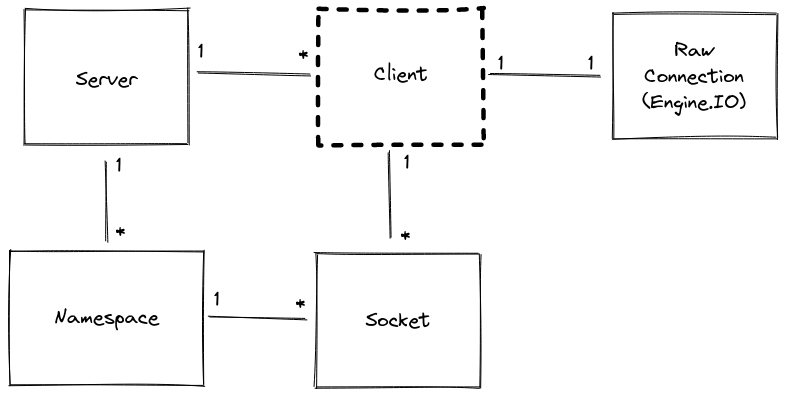
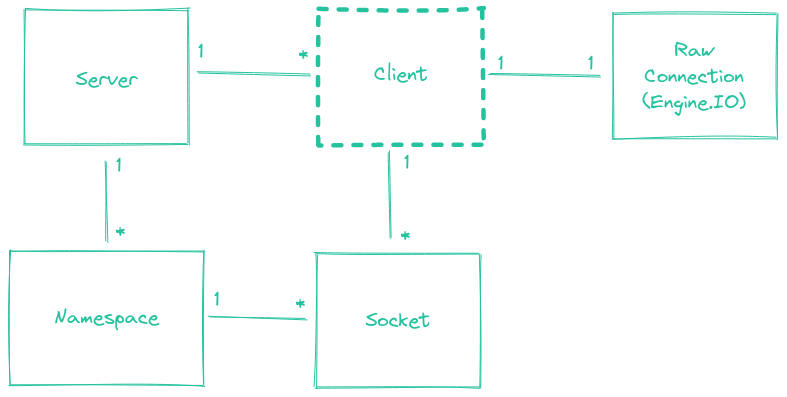
Client クラスは、受信トランスポート (engine.io) 接続を表します。Client は、異なる Namespace に属する複数の多重化された Socket に関連付けることができます。
属性
client.conn
<engine.Socket>
基盤となる engine.io Socket 接続への参照。
client.request
engine.io 接続を開始した request への参照を返すゲッタープロキシ。Cookie や User-Agent などのリクエストヘッダーにアクセスするのに役立ちます。
エンジン
WebSocket / HTTP ロングポーリング接続を管理する Engine.IO サーバー。詳細についてはこちらをご覧ください。
ソースコードはこちらにあります:https://github.com/socketio/engine.io
イベント
イベント: 'connection_error'
v4.1.0 で追加
error<Error>
io.engine.on("connection_error", (err) => {
console.log(err.req); // the request object
console.log(err.code); // the error code, for example 1
console.log(err.message); // the error message, for example "Session ID unknown"
console.log(err.context); // some additional error context
});
このイベントは、接続が異常に閉じられたときに発行されます。考えられるエラーコードのリストは次のとおりです。
| コード | メッセージ |
|---|---|
| 0 | "トランスポート不明" |
| 1 | "セッションID不明" |
| 2 | "不正なハンドシェイクメソッド" |
| 3 | "不正なリクエスト" |
| 4 | "禁止" |
| 5 | "サポートされていないプロトコルバージョン" |
イベント: 'headers'
v4.1.0 で追加
headers<Object>ヘッダー名でインデックスされたヘッダーのハッシュrequest<http.IncomingMessage>受信リクエスト
このイベントは、セッションの**各** HTTP リクエスト (WebSocket アップグレードを含む) のレスポンスヘッダーを書き込む直前に発行され、カスタマイズすることができます。
import { serialize, parse } from "cookie";
io.engine.on("headers", (headers, request) => {
if (!request.headers.cookie) return;
const cookies = parse(request.headers.cookie);
if (!cookies.randomId) {
headers["set-cookie"] = serialize("randomId", "abc", { maxAge: 86400 });
}
});
イベント: 'initial_headers'
v4.1.0 で追加
headers<Object>ヘッダー名でインデックスされたヘッダーのハッシュrequest<http.IncomingMessage>受信リクエスト
このイベントは、セッションの**最初**の HTTP リクエスト (ハンドシェイク) のレスポンスヘッダーを書き込む直前に発行され、カスタマイズすることができます。
import { serialize } from "cookie";
io.engine.on("initial_headers", (headers, request) => {
headers["set-cookie"] = serialize("uid", "1234", { sameSite: "strict" });
});
非同期操作を実行する必要がある場合は、allowRequest オプションを使用する必要があります。
import { serialize } from "cookie";
const io = new Server(httpServer, {
allowRequest: async (req, callback) => {
const session = await fetchSession(req);
req.session = session;
callback(null, true);
}
});
io.engine.on("initial_headers", (headers, req) => {
if (req.session) {
headers["set-cookie"] = serialize("sid", req.session.id, { sameSite: "strict" });
}
});
こちらもご覧ください
属性
engine.clientsCount
v1.0.0 で追加されました
現在接続されているクライアントの数。
const count = io.engine.clientsCount;
// may or may not be similar to the count of Socket instances in the main namespace, depending on your usage
const count2 = io.of("/").sockets.size;
メソッド
engine.generateId
新しいセッション ID を生成するために使用される関数。デフォルトは base64id です。
const uuid = require("uuid");
io.engine.generateId = () => {
return uuid.v4(); // must be unique across all Socket.IO servers
}
engine.handleUpgrade(request, socket, head)
v1.0.0 で追加されました
request<http.IncomingMessage>受信リクエストsocket<stream.Duplex>サーバーとクライアント間のネットワークソケットhead<Buffer>アップグレードされたストリームの最初のパケット (空の場合もあります)
このメソッドは、HTTP アップグレードを挿入するために使用できます。
Socket.IO サーバーとプレーン WebSocket サーバーの両方を使用した例
import { createServer } from "http";
import { Server as WsServer } from "ws";
import { Server } from "socket.io";
const httpServer = createServer();
const wss = new WsServer({ noServer: true });
const io = new Server(httpServer);
httpServer.removeAllListeners("upgrade");
httpServer.on("upgrade", (req, socket, head) => {
if (req.url === "/") {
wss.handleUpgrade(req, socket, head, (ws) => {
wss.emit("connection", ws, req);
});
} else if (req.url.startsWith("/socket.io/")) {
io.engine.handleUpgrade(req, socket, head);
} else {
socket.destroy();
}
});
httpServer.listen(3000);
engine.use(middleware)
v4.6.0 で追加されました
新しい Express ミドルウェア を追加します。
io.engine.use((req, res, next) => {
// do something
next();
});
ミドルウェアは、アップグレードリクエストを含む、受信 HTTP リクエストごとに呼び出されます。
express-session を使用した例
import session from "express-session";
io.engine.use(session({
secret: "keyboard cat",
resave: false,
saveUninitialized: true,
cookie: { secure: true }
}));
helmet を使用した例
import helmet from "helmet";
io.engine.use(helmet());